Every household should have the necessary electrical supplies to prevent any possibility of safety hazards. Knowing what type of electrical tape to add to your tool kit is part of ensuring the safety of yours and your family.
Here are the four types of electrical tape you should be familiar with.
Different Types of Electrical Tape
1. Vinyl
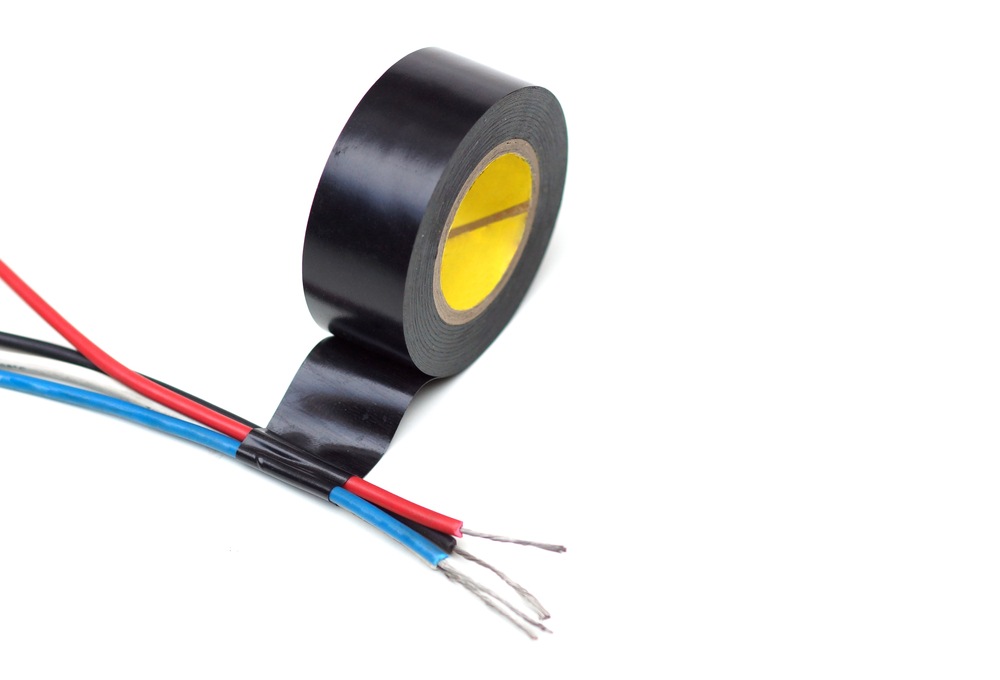

Most US homes have this type of electrical tape since the abrasion-resistant polyvinyl chloride backing makes it both flexible and durable. It’s perfect for insulating the wire and electrical connections in electrical tapping.
You can use them for protecting against moisture and repairing little nicks and cuts. They also withstand alkalis and acids like a champ.
2. Rubber

Rubber tape is generally non-adhesive but sticks to itself. This characteristic allows it to be extended around a cable completely with elastic tension against the backing.
You can use this type of tape to splice and terminate cables or wire-rated 69-kV at most.
Since rubber tape is water-resistant, it’s great for humid environments while the excellent electrical insulation makes it an effective wetness barrier.
3. Varnished Cambric

Built of woven cotton cloth, varnished cambric is covered with electrical insulating coatings and primed with oil. You may insulate electrical currents easily without the risk of being injured by the power that transfers via the wire.
The varnished cambric tape is perfect for corners, covering bolts, and other uneven edges that may cut into a less sturdy electrical tape. This is a great option for mechanical safety around the car, house, or workplace. You will find it puncture-resistant as well.
4. Mastic

Mastic is the part of the tape that forms the spongy area between the backing and the adhesive. This is used to build mastic pads inserted between layers to create the second layer of the insulation assembly.
When looking for versatility, a mastic tape is your go-to choice. There is either a vinyl backing or a rubber backing or no backing at all.
These tapes are often used by seasoned electricians as they adhere effortlessly and can be manipulated to fit in constricted places or around strangely shaped elements.
Mastic tape insulates metals, rubbers, and synthetic cable jackets. With great moisture and UV-resistant capabilities, they are a valued choice for outdoor wiring needs.
Electrical tape adhesive options
Non-adhesive

Non-adhesive electrical tapes don’t contain an applied adhesive. They are self-adhering and depend on a high coefficient of friction to stay adhered.
Acrylic

These adhesives offer great environmental resistance and quicker setting times compared to other resin systems. Surfaces do not need any pretreatment and they have a nice sheer and peels strength.
Hot melt/heat activated

Heat-activated adhesives become sticky when applying heat. They may get softer but not essentially melt. Hot melt adhesives can recurrently get softer and melt by heat and get harder by cooling. Cooling facilitates the repositioning of the adhesive’s portions while assembling.
Silicone
![]()
Silicone adhesives have a high degree of flexibility and quite high-temperature resistance of 600 degrees Fahrenheit. These adhesives are available as pressure-sensitive applications but a few of them may need ventilation, ultra violation, or Electron beam radiation to cure.
Pressure-sensitive

These adhesives are permanently and aggressively sticky at room temperature in dry conditions. Pressure-sensitive adhesives adhere strongly to various types of surfaces upon contact, requiring just the application of finger or hand pressure.
Electrical tape career options
Glass and fiberglass cloths
Glass and fiberglass cloth tapes are like cloth carriers but reinforced with glass or fiberglass components to improve their heat resistance capability to more than 300 degrees Fahrenheit.
Foam

Adhesive-coated polyolefin foams contain an adhesive secured by a liner in the structure of the tape. They provide good electrical conductivity with cushioning or recovery features. These compressible, electrical tapes are capable of filling gaps and perfect for metal or metal-plated surfaces.
PET/Polyester

Puncture-resistant and conformable with good electrical qualities, these tapes use a PET or polyester backing in the structure.
Fluoropolymer

Fluoropolymer films, layers, or coatings have plastics like polytetrafluoroethylene or polyvinylidene fluoride. They are used in applications that need higher chemical resistance, good dielectric attributes, and water and stain repellent features.
Metal foils

These shielding tapes contain aluminum reinforced, aluminum, or lead backings. You will need them for applications like static charge removal, grounding, and point-to-point electrical contact.
Films

Acrylic films are transparent, UV resistant, and made of plastic resins. Polyimide films contain average heat resistance and are comparatively thin. You can apply these films at low temperatures and use them for wave solder masking.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride)

PVC-backed electric tapes have the same properties as rubber but they are cheaper and more chemically resistant. When used for electrical insulation, they should be plasticized to improve their insulating attributes.
Cloth
Cloth materials such as cotton can be used as a carrier option to enhance tensile strength, heat resistance, and electrical resistance.
Polyimide
Polyimide film keeps great physical, mechanical, chemical, and electrical attributes in a broad range of physical environments. They are quite handy layers for the making of flexible circuit materials.
Plastic/polymer
Plastic film carriers are combined with materials like aluminum and paper. There are 2 common types of plastics – thermoplastics, and thermosets.
Silicone
Silicone tapes use a solid backing in the structure of a tape, which is made of silicon. These tapes offer moisture-resistant, tight, and void-free electric insulation.
Things to Consider When You Choose an Electrical Tape
Tape Stretch
You have to choose an electrical tape that can stretch without losing its original shape. It’s useful for wrapping wire because you should often stretch the tape around the cable, which requires you to return to its original shape for a tight wrap. The lack of stretching can lead to broken tape and uncovered cables.
Color
If you are using various colors to label your wiring, make sure that you’re maintaining a suitable color code so your electrician doesn’t become confused by a random mixture of colors on the wiring. White and black electrical tape is perfect for normal repairs in your house.
Resilience
-
High-voltage resistance
You’ll need high-voltage resistance for working on major electrical appliances in your house. The finest tape for high-voltage applications is rubber that can resist 600 volts.
-
High-temperature resistance
Vinyl and rubber both tapes can handle high temperatures. Vinyl tape can withstand 220° F while rubber tape can do even better at a range of 176°-266° F.
-
Moisture and water resistance
Both rubber and vinyl tapes resist moisture and water but mastic tape is better than them.
-
Airborne contaminant prevention
Every type of electrical tape has this capability. While vinyl is less efficient, mastic is effective at minimizing the risk of airborne contaminants accumulation.
-
Chemical and harsh fluid resistance
Rubber and mastic electrical tape does not have this feature. However, vinyl tape is capable of resisting chemicals like alkalis and acids.
Convenient to use
You have to choose a tape that’s flexible and simple enough to use so you may stretch and firmly stick it around a wire that is short. Tapes can be hard to use if they rotate or curl while you drag them from the roll.
To solve this, consider using the mastic tape that fits effortlessly to the surface it is applied on. Also, check to see whether the tape can be torn by hand or not.
Adhesive strength
Generally, electric tape stays effective for up to five years before the adhesive starts to break down. Although reasons such as excessive temperature alterations, physical stress, and revelation to direct sunlight can decrease this span of effectiveness.
Monomeric vs polymeric
-
Monomeric tape
These tapes are built with small chain plasticizers that are easily affordable and excellent for lighter, everyday tasks. They can be of less quality compared to polymeric tape but are cheaper as well.
-
Polymeric tape
These tapes are made of long-chain plasticizers, which makes them super sturdy with the capability to give firmer seals that are pretty good at shielding against moisture and deterioration. With a voltage resistance of a minimum of 600 volts, they are great for applications that have high voltage as well.
Code Compliance
You need to familiarize yourself with your area’s building codes. Choose reliable electric tapes according to your area’s building codes.
FAQs
1. Where should I use electrical tape?
Ans. Electrical tape is generally used in do-it-yourself applications for making repairs and joins to shorter wire. In cold environments, you will have to use cold weather tape for better adhesion. You can use standard electrical tape in every other application such as indoor settings.
2. Can electrical tape substitute for wire nuts?
Ans. No, it can’t. Electrical tapes are good for insulating wire but they can’t hold wire together. Wire nuts involve twisting the wire together, signifying the wire holds themselves in position. The nut insulates the top and aids in stopping movement. You should not use electrical tape in place of wire nuts for safety reasons, and it is at risk of damage.
3. Can I use the Gorilla tape as an electrical tape?
Ans. No, you cannot use Gorilla tape as electrical tape. Electrical tape is non-conductive and Gorilla tape is conductive. Using Gorilla tape on the wire can be hazardous. You can use wire nuts and heat-shrink tubing as alternatives to electrical tape.
4. Are electric tapes flammable?
Ans. Yes, they are flammable. Electrical tapes are specifically designed to contain thermal features that prevent them from catching fire so easily. However, if they are exposed to temperatures more than 176 degrees Fahrenheit, then they can catch fire. It also depends on the type of tape and the material.








